了解一项新的工作或研究内容,文献精读是首选,而Nature系类文章技术含金量高,文章内容条理清晰,精读一定会收获颇丰。
全基因组重测序是对已知基因组序列的物种进行不同个体的基因组测序,并在此基础上对个体或群体进行差异性分析。全基因组重测序的个体,通过序列比对,可以找到大量的单核苷酸多态性位点(SNP),插入缺失位点(InDel,Insertion/Deletion)、结构变异位点(SV,Structure Variation)位点,在全基因组水平上扫描并检测与重要性状相关的基因序列差异和结构变异,实现遗传进化分析及重要性状候选基因预测。
基于其研究的重要性,Google Scholar关键词搜索resequence,检索到《Resequencing of 31 wild and cultivated soybean genomes identifies patterns of genetic diversity and selection》,《Resequencing 302 wild and cultivated accessions identifies genes related to domestication and improvement in soybean》,现选择第一篇精读。
关键点总结
测序相关
- Approximately ×5 depth and >90% coverage.
- Previous reports have shown that the SNP calling accuracy from resequencing data is ~95–99% (Wang, J. et al. The diploid genome sequence of an Asian individual. Nature 456,60–65 (2008);Xia, Q. et al. Complete resequencing of 40 genomes reveals domestication events and genes in silkworm (Bombyx). Science 326, 433–436 (2009)).
- D-value (Tajima’s D) distribution was significantly higher that indicating a significant loss of rare SNPs, which may be due to reduced recombination within the LD blocks.
- Divergence index (FST) value allowed us to identify genomic regions of large FST value, which signified areas having a high degree of diversification.Subregions that have very high FST values may provide an indication of the functional genes or alleles involved.
- A genome-wide sequencing comparison to reveal haplotype sharing could provide a unique tool to identify introgression events in the history of these cultivars.
- Previous studies have indicated that whole genome duplication (WGD) events can cause gene loss and rapid functional diversification.
大豆研究相关
- They have exceptionally high linkage disequilibrium (LD) and a high ratio of average nonsynonymous versus synonymous nucleotide differences (Nonsyn/Syn).
- There was a recent history of introgression from wild soybean.
- Human selection probably had a strong impact on the genetic diversity in the cultivated soybeans.
- Genome-wide analyses showed the opposite: we found that the low-frequency alleles were less abundant among the wild as compared to the cultivated accessions.
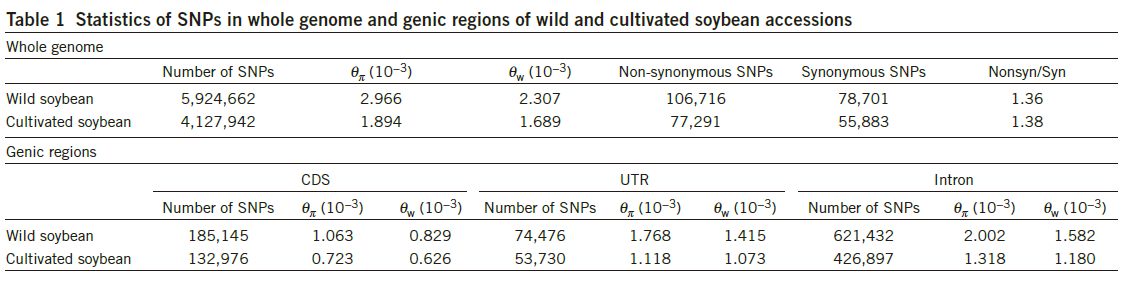
- In comparison with other crops, SNP analysis showed that the cultivated soybean exhibited a lower diversity (cultivated soybean: 1.89 × 10−3; rice: 2.29 × 10−3; corn: 6.6 × 10−3).
- The average distance over which LD decays to half of its maximum value in soybean was substantially longer than that of all plants analyzed
to date. - SNP analyses in the LD blocks showed that there was a lower SNP ratio in long LD blocks as compared to the whole genome in both wild and cultivated.
- Allelic diversity in wild soybeans was higher than in cultivated soybeans across the entire genome.
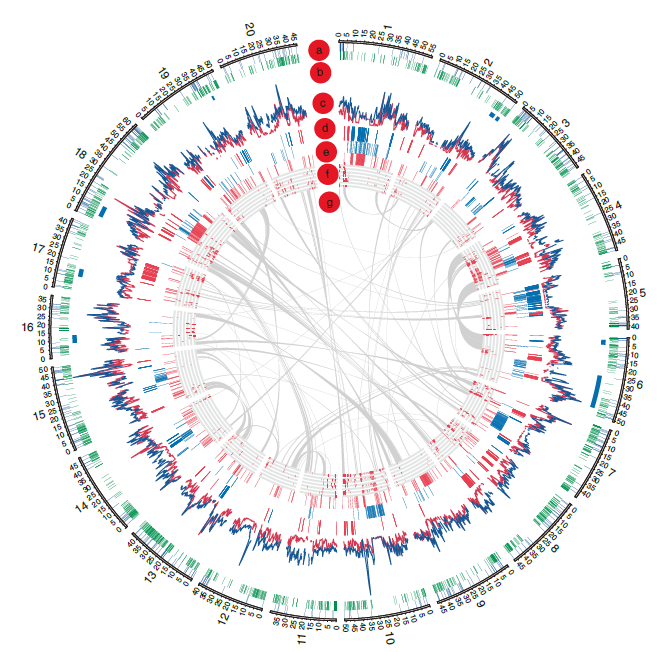
- Only ~3% of the total SNPs identified were present in coding regions. The remaining ~97% SNPs were in noncoding regions.
- The presence of a higher Nonsyn/Syn value at the whole-genome level and more large-effect mutations suggested that the soybean genome had accumulated a higher ratio of deleterious mutations.
- High LD(long LD blocks) would result in the lack of effective recombination; consequently, deleterious mutations could not be eliminated and would accumulate.
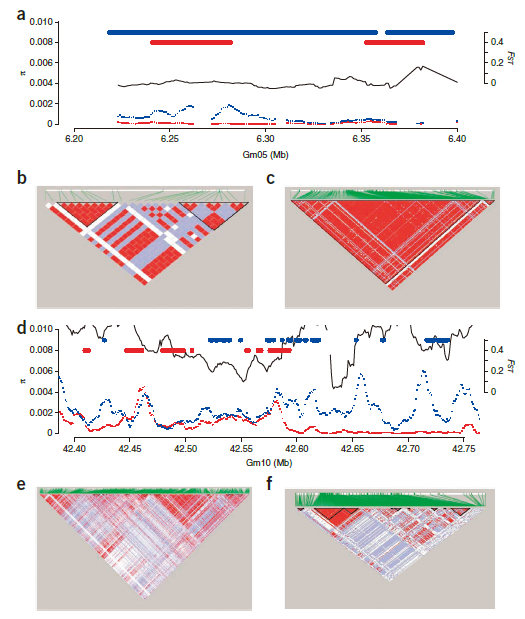
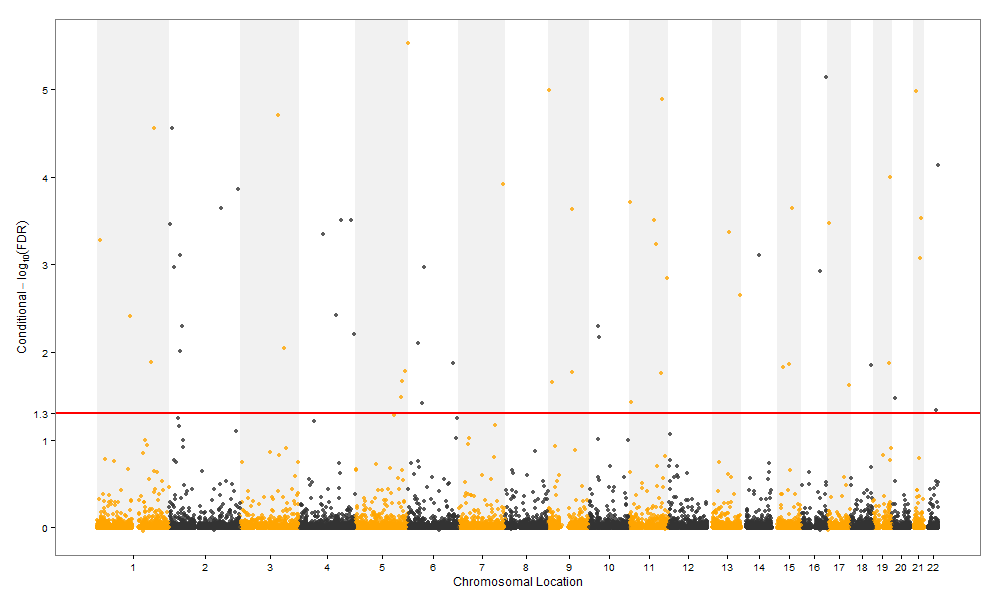
- Selection signals during domestication and improvement.
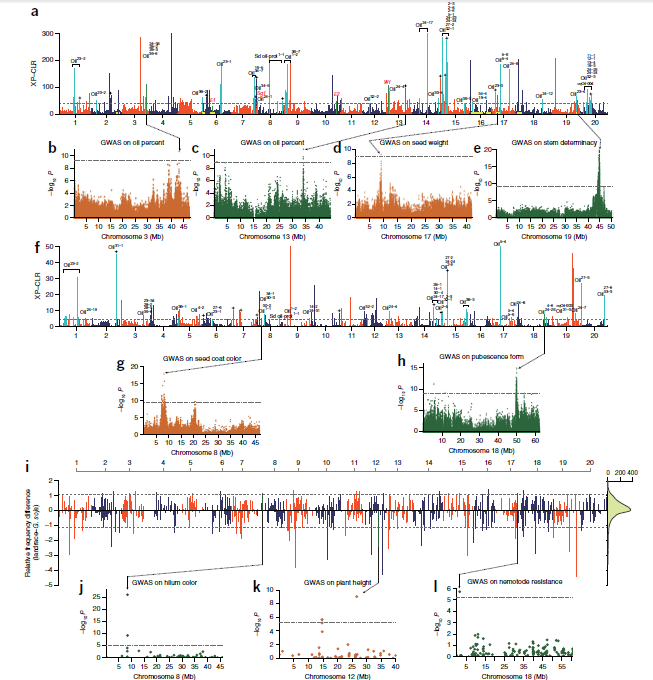
分析大致流程
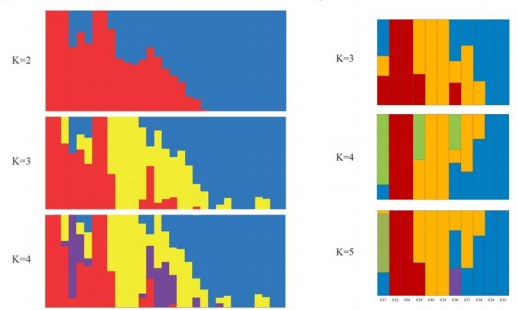
- 进化相关工作,包括phylogenetic tree(iTO),principle component analysis(PCA),population structure(Bayesian clustering analysis).
- Whole-genome SNP analysis (using the parameter θπ) and the distribution of genome-wide diversity.
- High linkage disequilibrium and genomewide patterns of nucleotide diversity(Selection and introgression).
- Genome duplication(copy number variations (CNVs)) and Gene content variation.
涉及软件
- STRUCTURE,Bayesian clustering program,http://pritchardlab.stanford.edu/structure.html
- Haploview,LD analysis,https://www.broadinstitute.org/scientific-community/science/programs/medical-and-population-genetics/haploview/haploview
- AUGUSTUS ,基因注释,http://bioinf.uni-greifswald.de/augustus/
- GeneWise and Genomewise,http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC479130/ ,http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/psa/genewise/
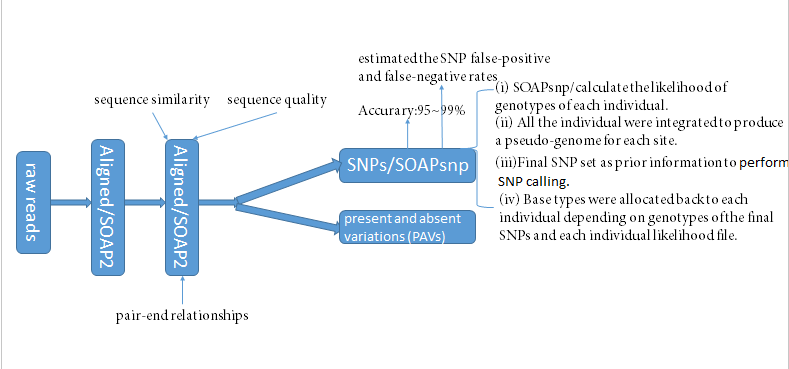
GeneWise, which predicts gene structure using similar protein sequences, and Genomewise, which provides a gene structure final parse across cDNA- and EST-defined spliced structure. Both algorithms are heavily used by the Ensembl annotation system. The GeneWise algorithm was developed from a principled combination of hidden Markov models (HMMs). Both algorithms are highly accurate and can provide both accurate and complete gene structures when used with the correct evidence. - SOAP and SOAPsnp,Short Oligonucleotide Alignment Program(45-bp or 76-bp), http://soap.genomics.org.cn/;
- BWA,Paired-end sequencing reads mapping,http://sourceforge.net/projects/bio-bwa/files/
- SAMtools,SNP detectionhttp://www.htslib.org/,http://biobits.org/samtools_primer.html
- Picard package,Duplicated reads filtered,http://picard.sourceforge.net/
- BEDtools,coverage of sequence alignmentshttp://bedtools.readthedocs.org/en/latest/
- Genome Analysis Toolkit (GATK),SNP/Indel calling,https://www.broadinstitute.org/gatk/gatkdocs/org_broadinstitute_gatk_tools_walkers_genotyper_UnifiedGenotyper.php
- ANNOVAR,SNP annotationhttp://annovar.openbioinformatics.org/en/latest/
- EIGENSOFT,Principal component analysis (PCA) of whole-genome SNPshttp://genetics.med.harvard.edu/reich/Reich_Lab/Software.html
- PLINK,Whole genome association analysis toolset,http://pngu.mgh.harvard.edu/~purcell/plink/
- GAPIT,Genome Association and Predictionhttp://www.maizegenetics.net/#!gapit/cmkv
- manhattan plot,https://pods.iplantcollaborative.org/wiki/display/eot/Make+manhattan+plot+with+ggplot2+script,http://blog.how-to-code.info/r/Manhattan-plot.html
内容补充链接
- Tajima’s D,https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tajima%27s_D;http://baike.baidu.com/link?url=hkRPQcUtBVMTVhMl2wzKGLy5QtDcrMwonUV7CspqxqdphkGztrSNFZLiUYazq6oz6rxZyVoy1YhHjexhi9Op9_.
- Penn State University Center for Comparative Genomics and Bioinformatics,http://www.bx.psu.edu/miller_lab/
