简介
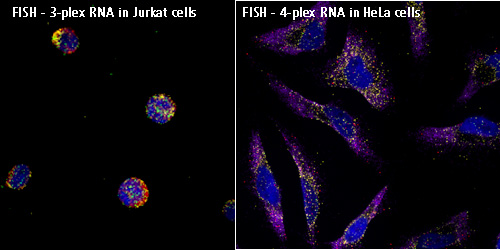
荧光原位杂交(fluorescence in situ hybridization,FISH)是在20世纪80年代末在放射性原位杂交技术的基础上发展起来的一种非放射性分子细胞遗传技术,以荧光标记取代同位素标记而形成的一种新的原位杂交方法。探针首先与某种介导分子(reporter molecule)结合,杂交后再通过免疫细胞化学过程连接上荧光染料。FISH的基本原理是将DNA(或RNA)探针用特殊的核苷酸分子标记,然后将探针直接杂交到染色体或DNA纤维切片上,再用与荧光素分子偶联的单克隆抗体与探针分子特异性结合来检测DNA序列在染色体或DNA纤维切片上的定性、定位、相对定量分析。FISH具有安全、快速、灵敏度高、探针能长期保存、能同时显示多种颜色等优点,不但能显示中期分裂相,还能显示于间期核。同时在荧光原位杂交基础上又发展了多彩色荧光原位杂交技术和染色质纤维荧光原位杂交技术.。
Preparation and hybridization process – DNA
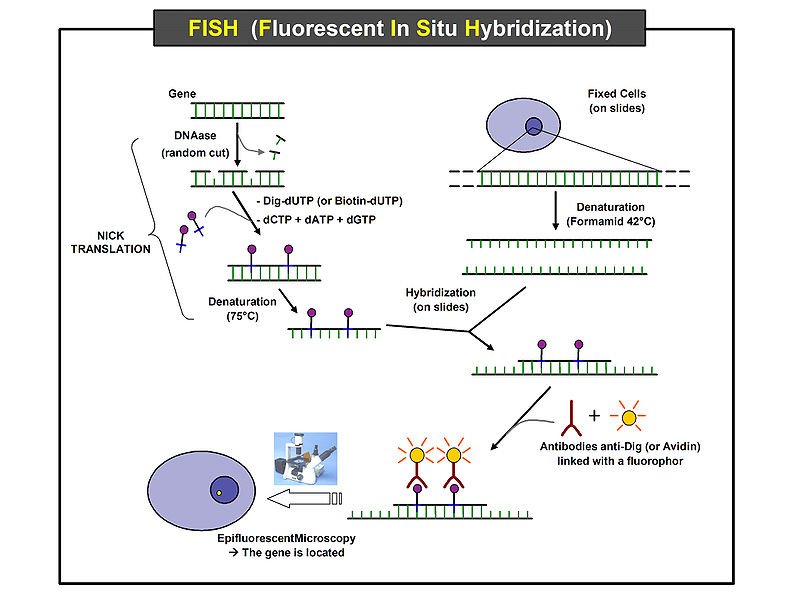
First, a probe is constructed. The probe must be large enough to hybridize specifically with its target but not so large as to impede the hybridization process. The probe is tagged directly with fluorophores, with targets for antibodies or with biotin. Tagging can be done in various ways, such as nick translation, or PCR using tagged nucleotides.
Then, an interphase or metaphase chromosome preparation is produced. The chromosomes are firmly attached to a substrate, usually glass. Repetitive DNA sequences must be blocked by adding short fragments of DNA to the sample. The probe is then applied to the chromosome DNA and incubated for approximately 12 hours while hybridizing. Several wash steps remove all unhybridized or partially hybridized probes. The results are then visualized and quantified using a microscope that is capable of exciting the dye and recording images.
If the fluorescent signal is weak, amplification of the signal may be necessary in order to exceed the detection threshold of the microscope. Fluorescent signal strength depends on many factors such as probe labeling efficiency, the type of probe, and the type of dye. Fluorescently tagged antibodies or streptavidin are bound to the dye molecule. These secondary components are selected so that they have a strong signal.
Difference between Southern Blot and Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) ?
FISH is performed on intact chromosomes through interphase or metaphase.it doesnt need DNA extraction and is performed on microscopic slides. its a type of kariotyping.its use is to determine the chromosomal abberations(numerical and structural) of a patient.
But,in Southern blotting you should first extract DNA of the specimen then cleave it with a restriction enzyme and then run on gel electrophoresis. the next step is to blot the DNA on a membrane and hybridaze it with a labeled probe. the use of suthern blot is in detecting mutations and restriction length fragment polymorphysms.
https://answers.yahoo.com/question/index?qid=20120611095540AA1YXhl
